20-2, 017-01, 1870s, Cabinet Card, Henry Wadsworth Longfellow (1807-1882) Writer




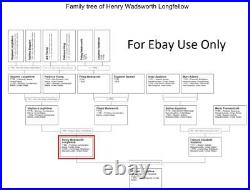
Family Tree (see last image). Henry Wadsworth Longfellow (February 27, 1807 - March 24, 1882) was an American poet and educator.
His original works include the poems "Paul Revere's Ride", "The Song of Hiawatha", and "Evangeline". He was the first American to completely translate Dante Alighieri's Divine Comedy and was one of the fireside poets from New England. Longfellow was born in Portland, District of Maine, Massachusetts (now Portland, Maine). He graduated from Bowdoin College and became a professor there and, later, at Harvard College after studying in Europe.
His first major poetry collections were Voices of the Night (1839) and Ballads and Other Poems (1841). He retired from teaching in 1854 to focus on his writing, and he lived the remainder of his life in the Revolutionary War headquarters of George Washington in Cambridge, Massachusetts. His first wife, Mary Potter, died in 1835 after a miscarriage. His second wife, Frances Appleton, died in 1861 after sustaining burns when her dress caught fire. After her death, Longfellow had difficulty writing poetry for a time and focused on translating works from foreign languages.
Longfellow wrote many lyric poems known for their musicality and often presenting stories of mythology and legend. He became the most popular American poet of his day and had success overseas.
He has been criticized for imitating European styles and writing poetry that was too sentimental. List of works: "The Village Blacksmith" (manuscript page 1) Outre-Mer: A Pilgrimage Beyond the Sea (Travelogue) (1835) Hyperion, a Romance (1839) The Spanish Student. A Play in Three Acts (1843) Evangeline: A Tale of Acadie (epic poem) (1847) Kavanagh (1849) The Golden Legend (poem) (1851) The Song of Hiawatha (epic poem) (1855) The Legend of Rabbi Ben Levi (1863) The New England Tragedies (1868) The Divine Tragedy (1871) Christus: A Mystery (1872) The Arrow and the Song (poem) Poetry collections: Voices of the Night (1839) Ballads and Other Poems (1841) Poems on Slavery (1842) The Belfry of Bruges and Other Poems (1845) The Seaside and the Fireside (1850) The Poetical Works of Henry Wadsworth Longfellow (London, 1852), with illustrations by John Gilbert The Courtship of Miles Standish and Other Poems (1858) Tales of a Wayside Inn (including the "second flight" of Birds of Passage) (1863) Household Poems (1865) Flower-de-Luce (1867) Three Books of Song (including the second part of Tales of a Wayside Inn) (1872) Aftermath (comprising the third part of Tales of a Wayside Inn and the "third flight" of Birds of Passage) (1873) The Masque of Pandora and Other Poems (1875) Kéramos and Other Poems (1878) Ultima Thule (1880) In the Harbor (1882) Michel Angelo: A Fragment (incomplete; published posthumously) Translations: Coplas de Don Jorge Manrique (Translation from Spanish) (1833) Dante's Divine Comedy (Translation) (1867) Anthologies: Poets and Poetry of Europe (Translations) (1844) The Waif (1845) Poems of Places (1874). Professor Edwin Emerson, Troy, NY.Card size: 4.25" x 6.5". Was a style of photograph which was widely used for photographic portraiture after 1870. It consisted of a thin photograph mounted on a card typically measuring 108 by 165 mm (4+1? The carte de visite was displaced by the larger cabinet card in the 1880s.
In the early 1860s, both types of photographs were essentially the same in process and design. Both were most often albumen prints, the primary difference being the cabinet card was larger and usually included extensive logos and information on the reverse side of the card to advertise the photographer's services. However, later into its popularity, other types of papers began to replace the albumen process.Despite the similarity, the cabinet card format was initially used for landscape views before it was adopted for portraiture. Some cabinet card images from the 1890s have the appearance of a black-and-white photograph in contrast to the distinctive sepia toning notable in the albumen print process. These photographs have a neutral image tone and were most likely produced on a matte collodion, gelatin or gelatin bromide paper.
Sometimes images from this period can be identified by a greenish cast. Gelatin papers were introduced in the 1870s and started gaining acceptance in the 1880s and 1890s as the gelatin bromide papers became popular. Matte collodion was used in the same period. A true black-and-white image on a cabinet card is likely to have been produced in the 1890s or after 1900. The last cabinet cards were produced in the 1920s, even as late as 1924.
Owing to the larger image size, the cabinet card steadily increased in popularity during the second half of the 1860s and into the 1870s, replacing the carte de visite as the most popular form of portraiture. The cabinet card was large enough to be easily viewed from across the room when typically displayed on a cabinet, which is probably why they became known as such in the vernacular. Whatever the name, the popular print format joined the photograph album as a fixture in the late 19th-century Victorian parlor.
Please see scans for actual condition. (images 3,4 & 5 are for reference only).This Cabinet Card would make a great addition to your collection or as a Gift (nice for Framing). Newest Collections with FREE S&H. To see all my Postcards. To see all my Movie Items. To see all my Disney Items.
To see all my Baseball Items. To see all my Boy Scout Cards. To see all my Stereoview Cards. Add me to your Favorite Sellers and Sign up for my Newsletter. Ground Advantage (the old 1st class).
Please look at my other Auctions for more Collectibles of the 1800's-1900's. Get Supersized Images & Free Image Hosting. Create your brand with Auctiva's. Attention Sellers - Get Templates Image Hosting, Scheduling at Auctiva.